What is Liquid Staking
Liquid Staking is a concept that allows users to stake their tokens while still being able to use them for various activities, including participation in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols 1. Staking is when users hold and validate tokens on PoS blockchains (Proof-Of-Stake) to support the network's operations and maintain its security. By staking their tokens, users contribute to the consensus protocol by actively participating in the block validation process and getting rewarded for doing so. Staked tokens differ from liquid staked tokens since they’re locked up for a specific amount of time and therefore can’t be used until that period ends. On the other hand, liquid staking tokens (LSTs) are representations of staked tokens that can be freely used and traded while still earning rewards 1.
Difference between traditional staked tokens and liquid staked tokens
Traditional Staking
Locked up for a specific amount of time and therefore can’t be used until that period ends
Liquid Staked Tokens
LSTs can be freely used and traded on DeFi applications and users can still receive rewards.
Users can access their LSTs without having to wait for a specific staking period to end.
Examples of LSTs in Solana:
SolBlaze: SolBlaze is an important player in the Solana ecosystem and offers various tools like BlazeStake and BlazeRewards. Users are rewarded for staking with BlazeStake or using bSOL 2. SolBlaze also provides tools like SOL faucet, Status, which tracks the RPC speed of Solana providers, and Token Minter, where users can create their own SPL tokens.
JitoSOL: JitoSOL is the LST token associated with Jito, a Solana validator. Users are rewarded for staking with JitoSOL 3. Jito also conducted an airdrop to the initial users who chose to stake with them.
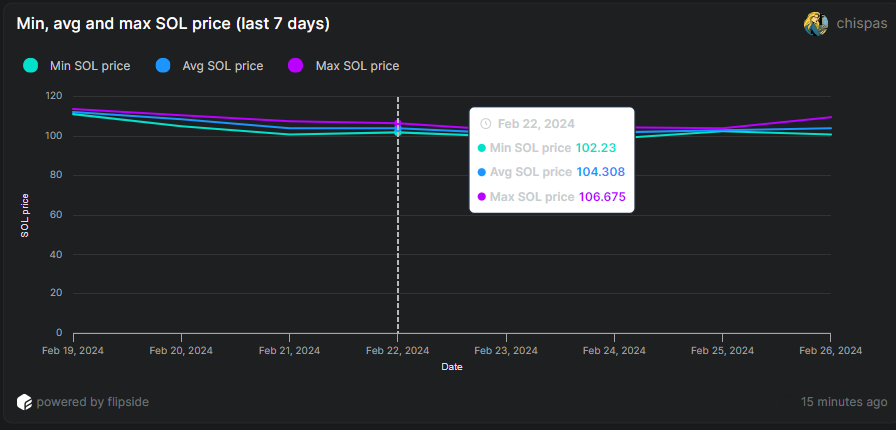
Curious what the daily minimum, average, and maximum price of BSOL has been for 7 days?
The chart above provides an estimate of the minimum, average, and maximum daily prices of bSOL over a 7-day period. This data is displayed in USD. For example, on Feb 22nd, the estimated minimum bSOL price was $113.74, the average was $115.88, and the maximum was $118.61.
It also shows a comparison with the minimum, average, and maximum daily prices of SOL, the native token of the Solana network, over 7 days.
You can also compare the prices of three liquid staking tokens (LSTs) - bSOL, JitoSOL, and mSOL - with the native Solana (SOL) token. Simply move your cursor throughout the chart to see the specific day you choose.
Usage of bSOL in DeFi Protocols
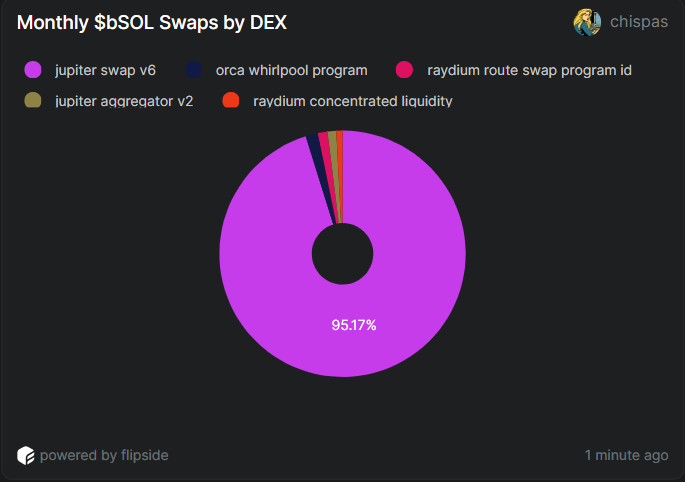
As said previously, Liquid staking tokens like bSOL can be sold, bought, and used in various DeFi protocols. One prominent decentralized exchange (DEX) for bSOL swaps is Jupiter Swap v6. In the last 30 days, there have been approximately 355.8k bSOL swaps involving 76.9k wallets. Notably, 95.17% of these bSOL swaps have been performed through Jupiter Swap v6.
Transaction Types for bSOL Swaps
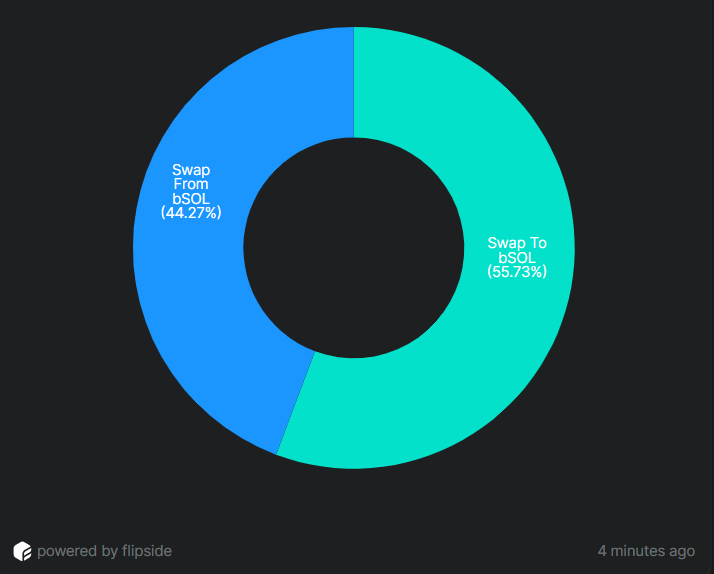
Since 2023, 55.73% of bSOL swaps have been buying transactions (swap to), while the remaining 44.27% have been selling bSOL transactions (swap from).
To provide an example, on Jan 27th, there were approximately 8.25k buying bSOL transactions involving 3.59k wallets.
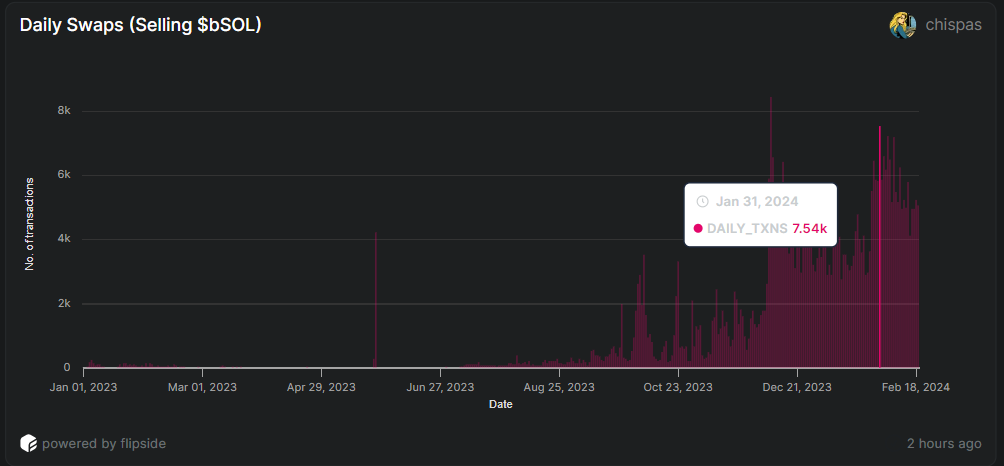
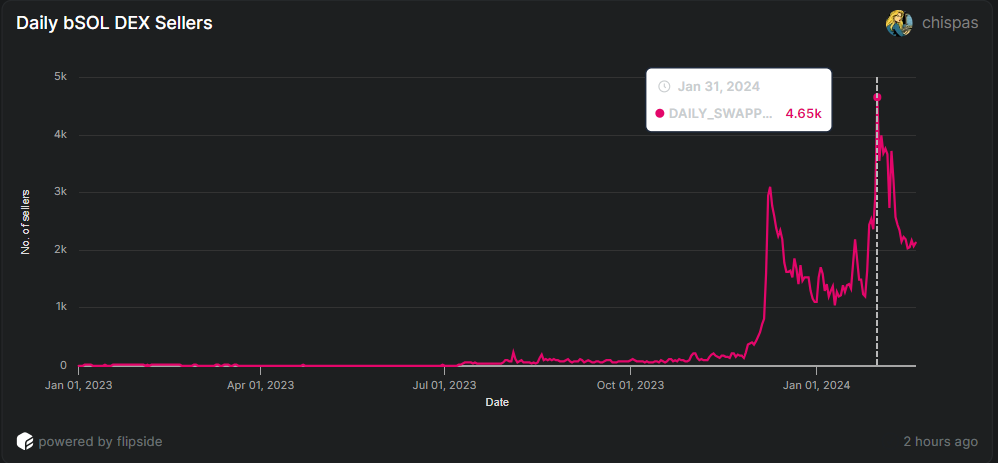
Let's also examine the selling bSOL transactions on January 31st. During this period, there were 7.54k transactions made by 4.65k user wallets.
Link to the dashboard, here
Since liquid staking and LSTs give more people access to the advantages of staking and DeFi, they have the potential to help in financial inclusion. Users who wish to engage in traditional staking typically need to fulfill some minimal conditions, such as possessing a considerable quantity of tokens or specific technical expertise. For those who do not have the means needed, this could provide obstacles.
Conversely, LSTs provide a more inclusive staking strategy. Users can still earn rewards from taking part in the consensus process even if they stake a smaller amount of tokens. Staking chances are now more accessible to a larger group of people, irrespective of their level of financial resources or technical proficiency, due to the decreased entrance barrier.
Furthermore, people can easily access the value of their staked assets due to the liquidity and utility of LSTs. People in areas with limited access to traditional financial institutions or those in need of readily available liquidity may find this beneficial. LSTs let anyone take part in the expanding DeFi movement and help the democratization of finance by offering a more flexible and accessible staking experience.
Conclusion
The growing interest in LSTs is evident from the increasing number of transactions and wallets involved in bSOL swaps. The ability to buy, sell, and use LSTs in various DeFi protocols enhances liquidity and promotes the composability of the DeFi ecosystem.
The key difference between traditional staked tokens and LSTs lies in their usability. Traditional staked tokens are locked and cannot be used or traded until the staking period ends, while LSTs can be freely used and traded on DeFi applications. This opens up new possibilities for users, allowing them to access the value of their staked assets without waiting for the staking period to end.
Developers and researchers are actively exploring new approaches and technologies to enhance the usability, security, and scalability of LSTs. As LSTs continue to gain traction, we can expect further advancements in the field of liquid staking, unlocking new avenues for financial inclusion and decentralized finance.
Sources:
Soares, X. (2023, June 30). What Is Liquid Staking in Crypto? Retrieved February 19, 2024, from https://beincrypto.com/learn/what-is-liquid-staking/#h-what-is-liquid-staking
SolBlaze (n.d.). Introducing SolBlaze, Building Solana's Ecosystem. Retrieved February 19, 2024, from https://solblaze.org/
JitoSOL (n.d.). MEV Powered Staking Rewards. Jito Network. Retrieved February 19, 2024, from https://www.jito.network/
Flipside Crypto. (2023, Feb 19). bSOL: Analysis for #ScribesHackathon (Chispas author). Retrieved February 19, 2024, from https://flipsidecrypto.xyz/chispas/parcl-v-3-analytics-parcl-v3-analytics-c-v7JZ
Disclaimer: This article is a submission for the technical research Scribes hackathon competition. It is important to note that the information provided in this article should not be considered financial advice. The author is not recommending or advising readers to engage in the purchase or interaction with liquid staking tokens, as all investments carry inherent risks. It is strongly encouraged that readers conduct their own research and exercise caution. This article is purely intended to be an informative piece.